The circulatory system is a network that transports blood throughout the body, carrying oxygen and nutrients to nourish each cell while also removing waste products. When the circulatory system is not functioning effectively, blood does not reach vital organs such as the brain, heart, kidneys, or limbs in a timely manner and in sufficient quantities, leading to a range of disorders in the body, with potential risks of stroke, organ failure, and even death.
Poor blood circulation is not a specific disease but a symptom of many underlying health issues. The following article will help you recognize the early signs of poor blood circulation, understand the causes, and provide effective and sustainable solutions for improvement.
What is poor blood circulation?
Blood circulation is the process by which the heart pumps blood through blood vessels to transport oxygen, hormones, and nutrients to each cell and carry waste products to the excretory organs. Poor blood circulation means that blood does not flow well to the parts of the body, causing ischemia in tissues, cell damage, and imbalances in organ function.
The consequences of poor blood circulation do not occur immediately but progress silently over time. If not addressed promptly, it can lead to serious consequences such as stroke, myocardial infarction, limb necrosis, kidney failure, and liver failure.
Signs of Poor Blood Circulation
Poor blood circulation often has no obvious symptoms in the early stages, but if you pay attention, you will notice the following changes in your body:
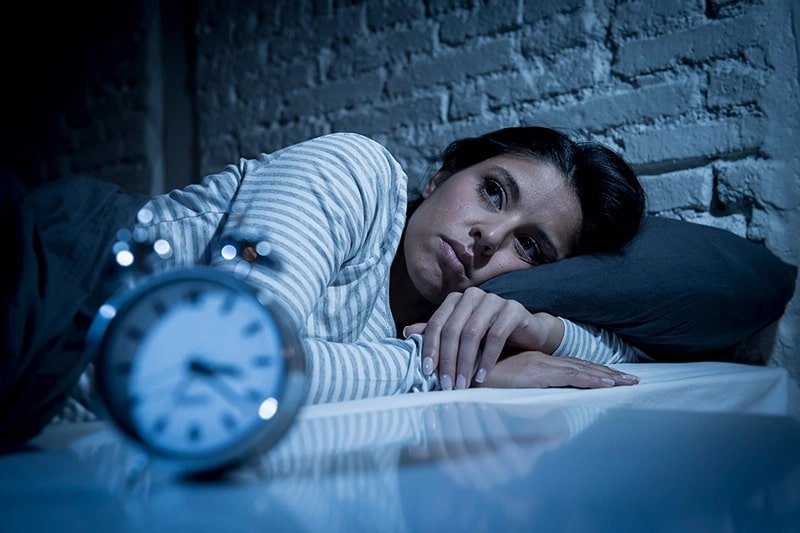
- Cold hands and feet, numbness, difficulty staying warm: This is the most common symptom. When blood does not circulate to the limbs, the palms and soles of the feet become cold even if the ambient temperature is not low. The sensation of numbness and tingling often occurs, especially after sitting or standing for a long time or at night.

Cold hands and feet are a sign of poor blood circulation
- Dizziness, vertigo, fatigue: Insufficient blood flow to the brain can lead to cerebral hypoxia, causing dizziness, loss of balance, accompanied by reduced concentration, forgetfulness, and memory decline.
- Pale, ashen skin: When blood circulation is weak, the skin does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, resulting in pale, dry skin, especially in the face, lips, and fingertips.
- Headaches, stiff and sore shoulders and neck: The muscles and nerves in the neck and shoulder area are very sensitive to a lack of blood. Poor blood circulation can cause muscle stiffness and prolonged aches in the neck, shoulders, and back.
- Swelling in the lower extremities: When blood is not pumped back to the heart efficiently, fluid accumulates in the lower parts of the body, such as the feet and ankles, causing swelling, heavy legs, and difficulty walking.
- Susceptibility to abdominal cold, poor digestion: The stomach and intestines also need blood to digest and absorb nutrients. When blood flow is poor, you are more likely to experience abdominal cold, indigestion, bloating, and poor appetite.
- Sexual dysfunction: Poor blood circulation affects the reproductive system, causing erectile dysfunction in men and decreased libido and menstrual irregularities in women.
Causes of Poor Blood Circulation
- Cardiovascular diseases: heart failure, coronary artery disease, heart valve stenosis, arrhythmias… reduce the heart’s pumping ability, leading to insufficient blood flow throughout the vascular system.
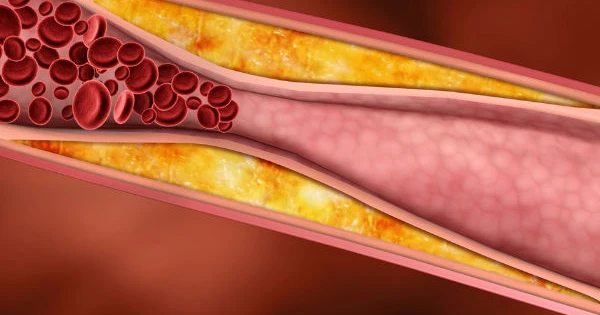
- Atherosclerosis: When the blood vessel walls become hardened due to high blood fat levels, bad cholesterol accumulates, causing the vessel lumen to narrow or become blocked, reducing blood flow and slowing circulation.
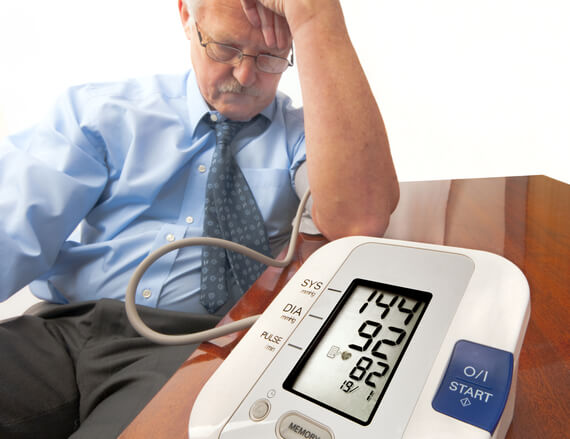
- Low or uncontrolled high blood pressure: Low blood pressure causes the blood to lack sufficient force to travel far. Conversely, high blood pressure damages blood vessels, which over time leads to impaired circulatory function.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar damages the vessel walls, reduces vascular elasticity, causes vessel narrowing, and disrupts blood circulation.
- Unhealthy living habits:
- Sitting for long periods, little physical activity
- Smoking, drinking alcohol
- Unhealthy eating, excess cholesterol
- Lack of sleep, prolonged stress
- Age and menopause: Older adults often have weakened cardiovascular and nervous systems. Postmenopausal women experience a gradual loss of estrogen – a hormone that helps protect blood vessels – increasing the risk of poor circulation.
How can poor blood circulation cause a stroke?
Poor blood circulation reduces blood flow to the brain, leading to:
- An increased risk of blood clot formation
- Temporary or prolonged brain oxygen deprivation
- Damage to the cerebral vessel walls, creating conditions for vessel rupture or blockage
If left untreated, this is a direct cause of stroke (cerebrovascular accident) – one of the leading causes of death today.
Safe and effective solutions to improve poor blood circulation
Change lifestyle and daily habits
- Increase physical activity: walk, do yoga, swim, or bike for 30 minutes/day
- Get enough sleep, go to bed early, avoid stress
- Quit smoking, limit alcohol and caffeine intake
- Drink enough water: at least 1.5–2 liters/day to help thin the blood and improve circulation
Diet to support blood circulation
Prioritize foods rich in antioxidants to help strengthen blood vessel walls and improve blood circulation:
- Fatty fish: salmon, mackerel contain omega-3
- Green vegetables and fruits: spinach, broccoli, pomegranate, orange, strawberry
- Nuts and seeds: walnuts, almonds, flaxseeds
- Garlic, ginger, turmeric: help dilate blood vessels and reduce inflammation
- Oats and whole grains: provide fiber, reduce blood fat
Limit salty foods, excessive oil and fat, processed foods, and refined sugar.

Eating scientifically is a way to reduce poor blood circulation.
Massage, acupressure, and foot soaking
- Gently massaging the hands and feet helps improve blood circulation.
- Soak your feet in warm water mixed with ginger or salt every evening to stimulate acupressure points.
- You can use natural essential oils such as lavender and peppermint to enhance relaxation effects.
Manage underlying medical conditions
- Regularly check blood pressure, blood sugar, and blood lipids.
- Follow treatment if you have cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or metabolic disorders.
- Do not stop medication without medical advice.
Use assistive products if necessary
Some dietary supplements contain herbal extracts such as ginkgo biloba, Salvia miltiorrhiza (danshen), Ligusticum wallichii (chuanxiong), safflower, black garlic, etc., which are believed to support blood circulation and protect blood vessels. However, it’s important to choose reputable products and consult a doctor before use.
When should you see a doctor?
If you experience any of the following signs, consult a healthcare professional for a blood circulation check:
- Prolonged numbness or tingling in hands and feet, with no apparent cause
- Pale, bluish skin, frequent chills
- Severe headaches, forgetfulness, dizziness
- Swelling in hands and feet that doesn’t subside with rest
- History of stroke or myocardial infarction (heart attack)
Early detection and timely intervention are crucial for preventing serious complications caused by poor blood circulation.
Poor blood circulation is a “silent enemy” because it progresses subtly but can lead to severe consequences like stroke, myocardial infarction, and organ failure. Therefore, proactively recognizing early signs, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and controlling risk factors are key to protecting your vascular health and overall well-being.
Listen to your body, pay attention to even small signs like cold hands and feet, fatigue, and headaches… as these could be early warning signs of a significant risk quietly developing. Improving your blood circulation is protecting your very life – start today.